
Sometimes, the smallest things carry the biggest stories.
Decades ago, as coconut shells piled up across rural landscapes in Asia, Haycarb saw more than just agricultural waste. We saw potential. What nature created in abundance – durable, carbon-rich shells could be transformed into something far more valuable. With innovation and responsible engineering, we began converting this by-product into high-quality activated carbon, helping industries around the world solve critical challenges sustainably.
Today, that same mindset drives our contribution to industries that rely on clean, efficient processes. From purifying condensate in steam systems to enabling cleaner air and water, Haycarb’s solutions are woven into the heart of modern industry.
This is the essence of transforming waste into solutions and challenges into opportunities!
Why Coconut Shells?
The question we get asked often.
The answer is clear. Coconut shells are unique in their properties making them ideal for producing high-performance activated carbon. The result is a material with high adsorption capacity, consistent performance, and a minimal environmental footprint, making it the go-to choice for industries committed to sustainability.

And where does this innovation make the real difference? In condensate purification – one of industry’s most critical yet often overlooked processes.
What is Boiler Condensate?
In a nutshell, Boiler Condensate is the liquid formed when steam generated by a boiler cools and condenses after transferring its heat energy. In industrial steam systems, steam delivers heat to various processes, and upon releasing this energy, it returns to its liquid state as condensate.
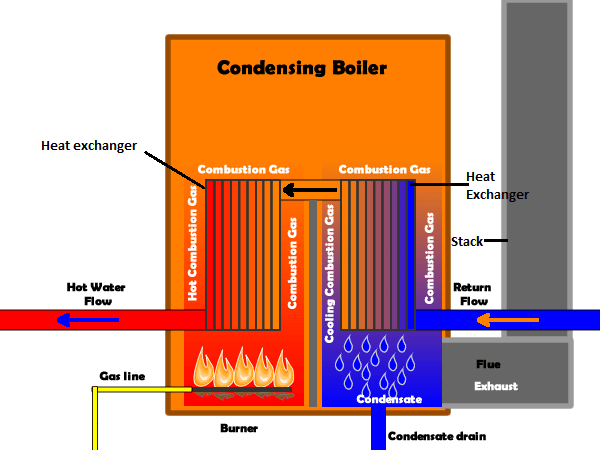
The Hidden Problem: Contaminated Boiler Condensate
What many don’t realize is the process the water undergoes throughout the boiler condensate cycle. Before even entering the system, both municipal water supplies and recycled condensates contain chlorine, oils, hydrocarbons, and other harmful contaminants. These impurities aren’t just simple “dirt”, instead they pose serious risks by damaging sensitive equipment including ion exchange resins, boiler tubes, and turbine blades.
As condensate circulates, it can accumulate additional organic impurities and oils, which accelerate corrosion, reduce boiler efficiency, and shorten equipment lifespan. Without proper treatment, these contaminants can lead to costly damage and system failures.
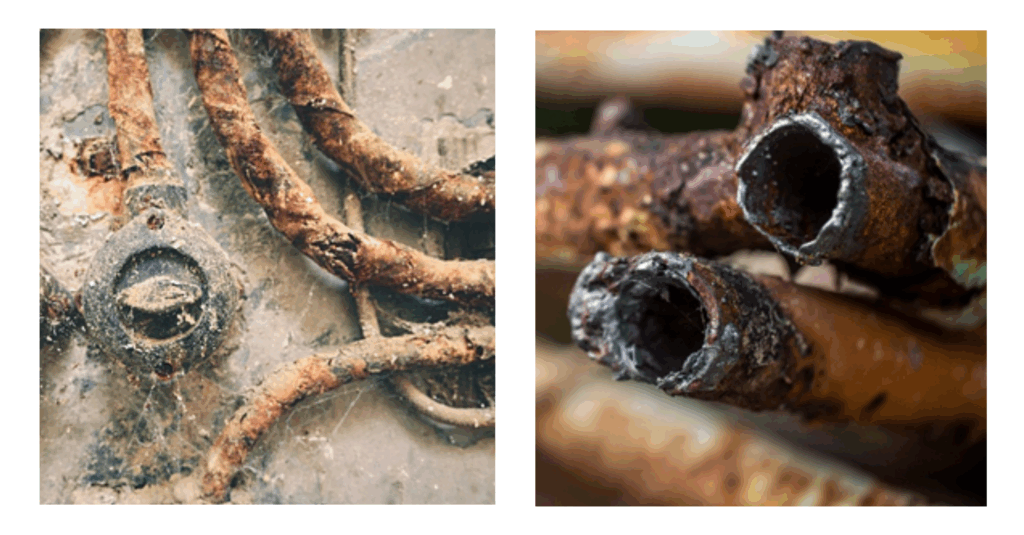

The Solution? Activated Carbon
This is where activated carbon makes a vital difference.
Engineered to adsorb and remove the harmful organic contaminants and oils from both fresh and recycled water used in boiler systems. The activated carbon acts like a magnet, trapping unwanted compounds before they can reach and damage ion exchange resins and other sensitive equipment.
What makes the difference? Purity. This high-quality carbon, produced with extremely low silica and ash content – two common contaminants found in other carbons that can cause scaling and wear inside boilers and turbines. Using such high-purity carbon allows industries to extend equipment lifespan and reduce costly maintenance.
The Bigger Picture
What was once seen as agricultural waste is now shaping industrial progress. Every drop of treated condensate means reduced corrosion, improved efficiency, and fewer breakdowns. At the forefront of this shift is Haycarb, delivering sustainable solutions that drives modern industry forward.
When cleaner condensate meets smarter thinking, industries win!
FAQs
- Can other materials be used instead of coconut shells for activated carbon?
Yes, but coconut shells offer better durability and sustainability, making them the best choice for industrial applications.
- How do contaminants in municipal water supplies affect industrial steam systems differently than those from recycled condensate?
Municipal water contaminants like chlorine enter fresh systems causing initial damage, whereas recycled condensate accumulates organic impurities over time, compounding wear and reducing system reliability.
- What is the typical chemical composition of boiler condensate?
Boiler condensate is mainly water, but it often contains trace amounts of carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides – depending on the type of fuel – sulfuric or hydrochloric acids. These contaminants result from the combustion process and can make the condensate mildly acidic and corrosive.
- How do organic contaminants enter the boiler condensate system?
Organic compounds such as oils, greases, or hydrocarbons can be introduced through process leaks, mechanical lubricants, or return line contamination especially in recycled systems. These compounds accumulate over time, threatening system integrity if not removed.
- Why is low ash and silica content important in activated carbon for condensate purification?
Ash and silica residues can leach into the condensate and cause scaling or abrasion inside critical equipment. Additionally, low-ash, low-silica activated carbon ensures cleaner operation and minimizes system wear.
- Can activated carbon actually remove acids or inorganic compounds from boiler condensate?
Activated carbon is highly effective at removing organic contaminants. However, for acidic components like sulfuric or hydrochloric acids, additional treatment methods such as dealkalization or neutralization may be needed in tandem with carbon filtration.
- How does carbon pore structure affect performance in condensate purification?
A well-developed microporous structure enhances the carbon’s ability to adsorb low-molecular-weight organic compounds.
- Does the pH of condensate impact activated carbon performance?
Yes. Extremely low pH (acidic conditions) can affect the lifespan of the carbon and its adsorption efficiency. However, coconut shell carbon tends to be more stable under mildly acidic conditions than some other carbon types.






